13 Best AI Detector Tools 2026: Text, Image & Deepfake Guide
The demand for reliable AI detection has surged in 2026 as generative AI becomes ubiquitous across text, images, audio, and video. From deepfakes circulating on social media to AI-generated essays in classrooms, the need to distinguish synthetic content from authentic human work has never been more critical. Newsrooms face pressure to verify viral content and combat misinformation. Educational institutions grapple with academic integrity while respecting student privacy. Enterprises worry about compliance liability when AI-generated content appears in contracts or communications. Content creators seek protection against unauthorized voice cloning and deepfake impersonation.
Users evaluating AI detectors care deeply about detection accuracy—the balance between false positives that unfairly flag legitimate work and false negatives that miss synthetic content. They need multi-modal support spanning text, images, video, and audio. Privacy and data handling policies matter tremendously, especially in education and healthcare. Seamless integration with existing workflows determines whether a tool gets adopted or abandoned.
This article provides a systematic comparison of 13 leading AI detectors, evaluating detection coverage, accuracy considerations, ease of use, integrations, privacy protections, and licensing models. We offer scenario-based recommendations to help you find the right tool for your specific needs, acknowledging that no single detector fits every use case.
Quick Tool Overview (detailed comparison follows in later sections):
Multi-Modal & Media Forensics
| Tool | Best For |
|---|---|
| Reality Defender | Enterprise multi-modal detection for newsrooms, platforms, and government agencies |
| Hive | Platform content moderation and brand safety at scale |
| Sensity | Visual deepfake detection for identity verification and brand protection |
| TrueMedia.org | Non-profit fact-checking tool for journalists and civil society |
| Deepware | Technical deepfake video analysis for researchers and security teams |
Text & Academic Integrity
| Tool | Best For |
|---|---|
| Turnitin | University-wide academic integrity with institutional LMS integration |
| GPTZero | Educator-focused AI writing detection with free tier |
| Copyleaks | Plagiarism + AI detection for education and enterprise |
| Winston AI | Content authenticity for writers, bloggers, and publishers |
| Originality.AI | Publisher and agency content verification workflows |
Image Detection
| Tool | Best For |
|---|---|
| AI or Not | Accessible image and audio checker for everyday users |
| Illuminarty | AI-generated image detection for creators and moderators |
Audio & Voice
| Tool | Best For |
|---|---|
| Resemble AI | Voice cloning and synthetic speech detection |
How We Evaluate the Best AI Detectors
Understanding the pain points different users face helps clarify what truly matters when evaluating AI detection tools.
Media organizations and platforms need to identify deepfake videos, synthetic voices, and manipulated images before misinformation spreads and editorial credibility suffers. Educational institutions worry about AI-generated essays undermining academic integrity, yet they must respect student privacy and avoid false accusations that damage trust. Enterprises and legal teams require auditable detection for compliance purposes, concerned about liability when AI-generated content violates regulations or creates reputational risk.
Content creators and brand owners increasingly face unauthorized deepfakes using their likeness, voice, or brand identity, requiring tools for legal protection and brand safety. Everyday users encountering suspicious media online want simple, accessible verification without technical expertise or subscription costs.
Across all these scenarios, users share fundamental concerns: detection reliability that minimizes both false positives penalizing legitimate work and false negatives missing synthetic content; transparency about detection methods and confidence levels; clear privacy and data handling policies; and integration capabilities that fit existing workflows rather than disrupting them.
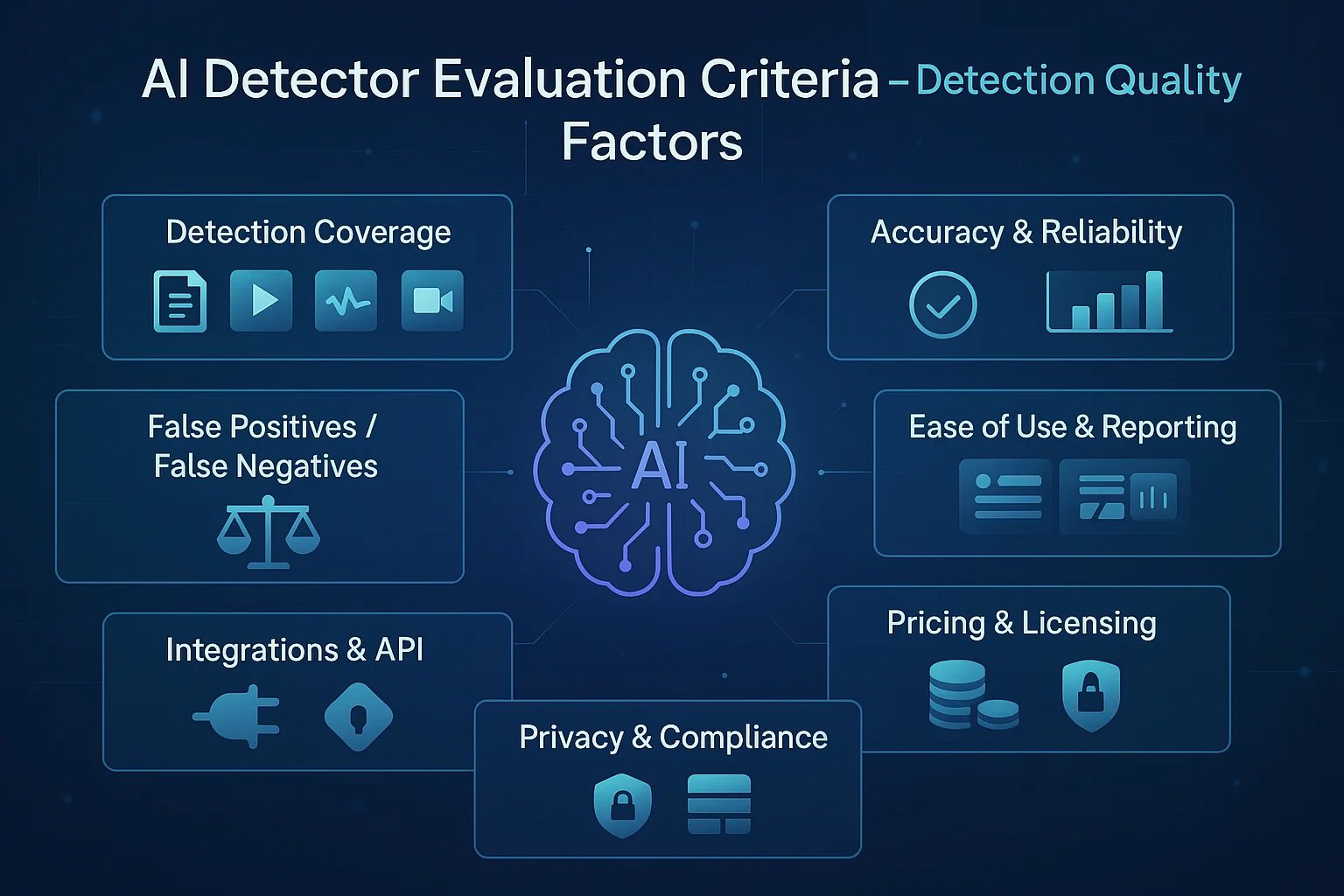
Evaluation Criteria for AI Detectors
Our evaluation framework examines several critical dimensions:
Detection Coverage assesses the types of content each tool supports—text, images, audio, video, or deepfake detection—and whether it handles single or multiple modalities. We examine which specific AI generation methods each tool targets, from LLM-generated text to GAN-produced images, voice cloning, and video synthesis.
Detection Quality and Accuracy receives qualitative assessment based on official claims, available third-party testing, and user reports. We acknowledge that exact accuracy rates cannot be fully verified independently in this article and express findings cautiously, noting where vendors provide transparency and where claims remain unsubstantiated.
False Positive and False Negative Trade-offs matter enormously in practice. Some tools lean conservative, flagging more content as AI-generated and producing more false positives. Others take a permissive approach, accepting more false negatives to avoid wrongly accusing users. We examine which approach each tool takes and implications for different risk contexts.
Ease of Use and Reporting evaluates interface intuitiveness, clarity of detection results, visualization quality, explainability of detection reasoning, and whether reports provide actionable insights or merely scores.
Integrations and Deployment Options include API availability, SDK support, browser extensions, LMS and CMS integrations, enterprise deployment models, and workflow automation capabilities that determine how smoothly a tool fits existing processes.
Compliance and Privacy examines data handling practices—whether uploaded content is stored, used for training, or shared with third parties—along with GDPR and CCPA compliance, audit trail capabilities, and suitability for regulated environments in education, healthcare, and legal contexts.
Pricing and Licensing receives qualitative description of subscription models, per-use pricing, enterprise contracts, and educational discounts. We avoid specific dollar amounts and direct readers to official sites for current pricing, while noting which tools offer free tiers, which require enterprise contracts, and which provide flexible options.
All tools reviewed in the detailed sections below are evaluated consistently using these criteria.
Top AI Detectors at a Glance
The AI detection landscape has evolved into a diverse ecosystem serving distinctly different needs. Enterprise-grade multi-modal platforms like Reality Defender, Hive, and Sensity handle millions of content items for newsrooms and platforms with serious scale requirements. Specialized deepfake and media forensics tools including Deepware, Illuminarty, and TrueMedia.org focus on visual content verification for specific threat scenarios.
Academic integrity solutions such as Turnitin, GPTZero, and Copyleaks integrate deeply with educational institutions, balancing detection capabilities with student privacy protections and institutional compliance needs. Content authenticity platforms like Winston AI and Originality.AI serve publishers and marketers verifying the originality of written content. Accessible free tools including AI or Not provide everyday users and individual creators with quick verification options. Specialized audio and voice detection from Resemble AI addresses synthetic speech threats.
Tools span a spectrum of accessibility and sophistication. Some require enterprise contracts with custom pricing and professional implementation support—Reality Defender, Hive, Sensity, and institutional Turnitin deployments fall into this category. Others offer subscription plans accessible to small teams and individuals, including GPTZero, Copyleaks, Winston AI, and Originality.AI. Several provide free tiers or public access suitable for casual verification, notably AI or Not and TrueMedia.org for fact-checkers.
Key differentiators across the 13 tools we review include detection modality—text-only versus image versus video versus audio versus comprehensive multi-modal support. Target user base varies dramatically between education-focused, journalism-oriented, enterprise-grade, and individual-user tools. Deployment models range from cloud API services to on-premises installations to simple browser tools. Accuracy-accessibility trade-offs balance enterprise-grade precision against quick public checks. Privacy and compliance features span from FERPA and GDPR compliance to minimal data handling for public tools.
Comprehensive Comparison Table
The following table provides structured overview across evaluation dimensions, helping you quickly identify candidate tools matching your scenario before diving into detailed reviews.
| Tool | Best For | Content Types | Detection Focus | Ease of Use | Pricing Model | Key Integrations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reality Defender | Newsrooms, platforms, government agencies | Text, image, video, audio, deepfakes | Multi-modal synthetic media | Enterprise interface with API | Self-serve + enterprise tiers | API, custom workflows, audit systems |
| Hive | Platform moderation, brand safety | Image, video, some text | Content safety and synthetic detection | Developer-friendly API | Usage-based API + free tools | API, SDK, moderation dashboards |
| Sensity | Identity verification, brand protection | Image, video deepfakes | Visual deepfake and manipulation | Enterprise platform | Enterprise sales model | API, threat intelligence feeds |
| TrueMedia.org | Journalists, fact-checkers, NGOs | Image, video, audio | Election integrity and misinformation | Simple web interface | Free for fact-checking | Web-based, minimal integrations |
| Deepware | General users, researchers, security teams | Video deepfakes (primarily visual) | Deepfake video detection | Browser-based scanner | Check official site | Browser, open-source components |
| Turnitin | Universities, colleges | Text | Plagiarism and AI writing | Institutional LMS integration | Institutional licensing | Canvas, Moodle, Blackboard, major LMS |
| GPTZero | K-12 and higher education | Text | AI-generated writing | Educator-friendly interface | Free tier + institutional plans | Google Classroom, LMS, Chrome extension |
| Copyleaks | Education and enterprise | Text, images | Plagiarism and AI detection | Intuitive with detailed reports | Subscription tiers | Canvas, Moodle, API, Chrome extension |
| Winston AI | Writers, publishers, bloggers | Text, images | Content authenticity | Simple web and extension | Subscription plans | Chrome extension, API |
| Originality.AI | Publishers, SEO professionals | Text | Content verification | Team workflow features | Credit-based subscription | Chrome extension, API, CMS plugins |
| AI or Not | Everyday users, creators | Image, audio, text, some video | Quick verification | Simple public web tool | Free tier + paid plans | Web-based interface |
| Illuminarty | Creators, moderators | Images, text | AI-generated content detection | Browser-based tool | Check official site | Web-based, batch processing |
| Resemble AI | Voice professionals, enterprises | Audio, voice | Voice cloning and synthetic speech | API-focused | Usage-based pricing | API, voice workflows |
This table enables horizontal scanning to shortlist 2-3 tools matching your needs before exploring detailed reviews in the next section.
In-Depth Reviews of the Best AI Detectors
Reality Defender
Reality Defender positions itself as an enterprise-grade multi-modal detection platform serving organizations facing serious deepfake and synthetic media threats. Typical users include newsrooms verifying user-submitted content, platforms moderating millions of uploads, government agencies monitoring disinformation campaigns, and large enterprises protecting brand reputation.
Core features include detection across text, images, audio, and video through an API-first architecture designed for workflow integration. The platform claims high accuracy on deepfake detection with explainable results showing which aspects of content triggered detection. High-volume processing capabilities support real-time verification needs, while audit trail features meet compliance requirements for enterprises and government users.
Limitations include pricing and feature tiers optimized for organizational use rather than individual casual verification, though self-serve options now exist. Detection methodology lacks full transparency, as with most commercial tools protecting proprietary techniques. Effectiveness varies by content type and generation method—what works well for one deepfake technique may miss others. Potential exists for false positives on heavily edited but authentic media, requiring human review of flagged content.
Best-fit use cases include fact-checking workflows in professional newsrooms, platform content moderation at scale handling user-generated content, government and NGO disinformation monitoring operations, and brand protection against deepfake impersonation targeting executives or public figures.
Reality Defender now offers self-serve web and API access with free trial credits, alongside enterprise contracts for larger deployments. Volume-based pricing scales from individual testing to institutional use. Check the official site for current plans and features. Commercial use permissions are typically included but should be verified based on your specific use case.
Get started with Reality Defender
Hive
Hive operates as an AI-powered content moderation platform with strong visual AI capabilities, serving platforms, social networks, marketplaces, and enterprises needing automated content classification alongside synthetic media detection.
The platform offers multi-modal detection covering images, video, and some text analysis. Pre-trained models address various content safety use cases beyond just AI detection, including inappropriate content filtering. API and SDK options enable easy integration into existing applications. Fast processing supports real-time moderation scenarios essential for user-generated content platforms. Comprehensive dashboards provide analytics and reporting for moderation teams.
Limitations include a business model primarily targeting platforms and enterprises via APIs, though public tools like web-based checkers and browser extensions are also available. Detection accuracy depends on specific content types, and the tool may have higher false negative rates in some scenarios, prioritizing platform usability over maximum sensitivity. Pricing scales with volume and may become costly for very high-traffic scenarios. Detection reasoning explanations are limited compared to tools focused solely on AI detection.
Best-fit use cases span social media and user-generated content platform moderation, e-commerce marketplace content screening before listings go live, app content safety ensuring community guidelines compliance, and brand safety for advertisers evaluating whether placement contexts meet brand standards.
Pricing uses usage-based API models with tiered plans suitable for various scale requirements. Enterprise contracts are available for larger deployments. Check the official site for current rates and licensing terms before commercial deployment.
Get started with Hive
Sensity
Sensity specializes in deepfake detection focusing on visual media—images and videos—as part of a multi-modal digital media intelligence platform. The platform targets enterprises, governments, and organizations concerned with identity fraud, political misinformation, and brand impersonation through synthetic media.
Advanced deepfake video detection capabilities form the core offering, with particular strength in detecting facial manipulation and face-swap techniques. Identity verification use cases leverage these capabilities to prevent synthetic identity fraud. Threat intelligence reports provide organizations with insights into emerging deepfake trends and attack patterns. API access enables automated screening workflows integrated into existing security infrastructure.
Trade-offs include specialization in visual deepfakes rather than text or audio, leaving organizations to supplement with other tools for comprehensive coverage. While the platform's core strength lies in face-centric threats, it also analyzes broader visual signals in synthetic media. Enterprise-oriented pricing and access models exclude individual users and small teams. Detection effectiveness varies significantly with deepfake generation quality and technique—state-of-the-art deepfakes remain challenging to detect reliably.
Ideal applications include identity verification for financial services preventing account takeover, political campaign monitoring detecting deepfake attacks on candidates, celebrity and executive brand protection against impersonation, and law enforcement investigations of synthetic identity fraud in criminal cases.
Sensity employs an enterprise sales model with custom pricing likely including professional services and threat intelligence subscriptions. Organizations should verify licensing terms for their specific use cases directly with the vendor.
Get started with Sensity
Copyleaks
Copyleaks combines plagiarism detection with AI content detection, serving both education and enterprise markets. Schools, universities, publishers, and businesses use the platform to verify originality and detect AI-generated content alongside traditional plagiarism.
The platform originally focused on text analysis, integrating AI detection with comprehensive plagiarism checking across multiple languages. It now also offers AI image detection capabilities that identify AI-generated or AI-altered images with pixel-level analysis. Major LMS integrations including Canvas, Moodle, and Blackboard enable seamless institutional deployment. API access supports custom workflows beyond standard integrations. Detailed similarity reports highlight suspected AI-generated sections alongside plagiarism matches, helping educators and editors make informed decisions.
Limitations include evolving multi-modal coverage—while text and images are well-supported, video and audio detection capabilities are less mature compared to specialized media forensics platforms. Accuracy of AI detection carries inherent uncertainty and may produce false positives on legitimate student or employee work, especially for non-native English speakers or technical writing. Detection effectiveness varies by AI model and writing style as models evolve. Reports require careful interpretation to avoid unfair accusations based solely on algorithmic outputs.
Best use cases include academic integrity enforcement in educational institutions with established review processes, content authenticity verification for publishers reviewing freelance submissions, employee communications review in regulated industries requiring content audits, and due diligence for content licensing ensuring purchased content is original.
Pricing offers subscription plans for individuals, educational institutions, and enterprises, with per-page or per-document pricing models available depending on use case. Educational discounts are typically offered to schools and universities. Verify current pricing and licensing details on the official site as plans evolve.
Get started with Copyleaks
AI or Not
AI or Not provides an accessible public-facing detection tool covering images, audio, text, and some video formats, designed for everyday users, content creators, and small teams wanting quick verification without enterprise contracts or steep learning curves.
The simple web interface requires no signup for basic checks, lowering barriers to entry. Support for multiple content types—images, text, audio, and some video/deepfake formats—provides more versatility than most free tools. A free tier with reasonable usage limits serves casual verification needs. Fast results with visual indicators make findings easy to interpret. Educational resources help users understand AI detection basics and limitations.
Trade-offs include detection accuracy likely lower than enterprise-grade tools, given the simplified approach and free access model. Limited explainability provides scores without detailed reasoning. No audit trails or advanced reporting features suit personal use but not institutional requirements. Free tier usage limits require paid plans for regular use. The tool is not suitable for high-stakes or legal use cases requiring defensible results.
Ideal applications include individual verification of suspicious images or audio encountered online, creator protection checking whether personal work has been copied and AI-modified, educators performing quick spot checks on assignments, and personal due diligence before sharing potentially misleading content on social media.
Pricing includes a free tier for basic checks with usage caps, plus paid plans for higher volume and additional features. Commercial use terms should be verified on the official site before deploying in business contexts, as free tool licenses often restrict commercial applications.
Get started with AI or Not
Resemble AI
Resemble AI specializes in voice cloning and speech synthesis technologies, offering built-in AI voice detection capabilities as part of its platform. The tool serves voice-over professionals, enterprises protecting voice intellectual property, and organizations monitoring for voice deepfakes and fraud.
Specialized audio and voice detection leverages deep expertise in speech synthesis mechanisms. The platform can identify cloned voices and synthetic speech with sophisticated analysis. API integration enables deployment into call centers, podcasting workflows, authentication systems, and other voice-dependent applications. Real-time detection capabilities support live verification scenarios like call center fraud prevention.
Limitations include narrow focus on audio and voice rather than text, images, or video, requiring supplemental tools for comprehensive protection. Detection accuracy varies significantly with voice cloning quality—amateur clones are easier to detect than professional-quality synthesis—and background noise or audio quality issues can affect results. False positives may occur with heavily processed but authentic audio. Pricing may be prohibitive for individual voice talent without enterprise backing.
Best-fit scenarios include voice authentication for secure systems requiring liveness detection, podcast and audiobook verification ensuring voice talent authenticity, call center fraud prevention detecting synthetic callers, brand protection for voice talent and celebrities combating unauthorized voice cloning, and media verification for audio journalism fact-checking voice clips.
Pricing likely follows usage-based or subscription models for API access, with potential enterprise contracts offering custom terms. Verify current pricing and commercial use permissions directly on the official site, as voice technology licensing can be complex.
Get started with Resemble AI
GPTZero
GPTZero has emerged as a leading AI text detection tool purpose-built for education, widely adopted by teachers, professors, and academic institutions to detect AI-generated student writing while respecting student privacy.
Specialized detection algorithms target ChatGPT and other LLM-generated text, optimized for academic writing contexts. A generous free tier supports individual educators with limited budgets. Batch document scanning enables efficient review of multiple assignments. Integrations with Google Classroom and major LMS platforms fit educational workflows seamlessly. Perplexity and burstiness metrics provide explainable detection, helping educators understand why content was flagged. A Chrome extension offers convenient access during grading.
Important limitations include text-only detection without multi-modal support. False positive risk exists, particularly on legitimate student work from non-native English speakers or students whose writing naturally exhibits low linguistic complexity. Detection effectiveness decreases as LLMs improve and students learn to paraphrase AI outputs, creating an ongoing arms race. The tool should not serve as the sole basis for academic misconduct charges—institutional policies should require corroborating evidence and student conversations.
Appropriate use cases include supplemental screening helping educators identify assignments warranting closer review, institutional academic integrity monitoring establishing baseline metrics, writing center consultations helping students understand how their writing appears to detection tools, and educational research studying AI writing prevalence and patterns.
Pricing includes a free tier for individual educators with usage limits suitable for classroom use. Institutional subscriptions are available for schools and universities requiring broader deployment, audit trails, and administrative features. Check the official site for pricing details and educational discounts. Ensure any deployment complies with student privacy laws including FERPA and COPPA.
Get started with GPTZero
Turnitin
Turnitin has long dominated plagiarism detection in higher education, and recently added AI writing detection capabilities to its established originality checking platform. The tool maintains strong institutional presence worldwide, particularly in universities and colleges.
Comprehensive originality checking combines an extensive plagiarism database, internet search, and AI detection in unified similarity reports. Deep integrations with major LMS platforms enable institutional-scale deployment administrators can manage centrally. Robust privacy and compliance features meet educational institution requirements including FERPA. Similarity reports highlight potential AI-generated content alongside traditional plagiarism matches, providing educators with complete context for evaluating submissions.
Limitations include AI detection being a newer addition with accuracy still evolving as the feature matures. False positives requiring instructor judgment remain a concern, especially for students with particular writing styles. Coverage focuses on text without image, video, or audio detection. Institutional subscription requirements mean individual educators or students cannot access the tool independently. Pricing can represent significant budget commitments for institutions, though costs scale with student population.
Best use cases center on university-wide academic integrity enforcement providing consistent standards across departments, large-scale assignment screening handling thousands of submissions during peak periods, graduate thesis verification ensuring original scholarship, and accreditation compliance documentation demonstrating institutional integrity measures.
Pricing operates exclusively through institutional licensing for universities and colleges, based on student FTE and selected features. FERPA compliance and student privacy protections are built into institutional agreements. Contact the vendor directly for educational institution pricing, as public pricing is not published.
Get started with Turnitin
TrueMedia.org
TrueMedia.org operates as a non-profit focused deepfake detection tool specifically designed for journalists, fact-checkers, and civil society organizations combating election misinformation and harmful synthetic media with transparent, accessible detection.
Multi-modal detection spans images, video, and audio, providing comprehensive coverage for media verification. Free public access supports fact-checking use cases, aligning with the non-profit mission of combating misinformation. Explainable detection results include confidence scores and reasoning, helping journalists understand detection basis for reporting. Educational resources about deepfakes and synthetic media help users develop media literacy. The platform is designed with journalistic ethics and transparency principles as core values.
Trade-offs include free service potentially having usage limits or slower processing during peak periods given resource constraints. Detection accuracy is transparently acknowledged as imperfect and evolving, with the organization openly discussing limitations—a refreshing approach but one that requires users to maintain appropriate skepticism. Limited enterprise features or commercial API access reflects the public interest mission. The tool is best suited for fact-checking and research rather than commercial content moderation.
Ideal scenarios include newsroom fact-checking of viral content during breaking news, election monitoring by NGOs and watchdog groups tracking campaign deepfakes, researcher analysis of deepfake prevalence and trends, and media literacy education in schools and communities teaching critical evaluation skills.
The platform is free for qualifying fact-checking and public interest use, supported by donations and grants. Verify acceptable use policies and attribution requirements on the official site, as non-profit tools often have specific usage guidelines to maintain mission alignment.
Get started with TrueMedia.org
Deepware
Deepware centers on deepfake video detection and provides a browser-based scanner accessible to general users, alongside open-source components and API features that appeal to researchers and security professionals.
Specialized deepfake video analysis examines visual content for manipulation indicators, with particular strength in facial deepfake detection. Deepware distinguishes itself by offering an open-source CLI scanner and sharing details about its model architecture, making it more transparent and research-friendly than many fully proprietary commercial tools. The browser-based scanning tool provides accessibility without complex installation. Support for researcher and developer use cases includes documentation suitable for technical evaluation. Detection confidence scores and visual analysis help users understand finding basis.
Limitations include a primary focus on visual deepfakes, especially faces, without the fully integrated multi-modal enterprise suite that tools like Reality Defender or Sensity provide. Detection accuracy is limited by rapidly evolving deepfake generation methods—new techniques may evade detection until analysis is updated. Higher false negative rates on state-of-the-art deepfakes are acknowledged. Limited commercial support or enterprise features reflect the research-oriented positioning.
Best applications include researcher analysis of deepfake detection methods for academic publications, security teams investigating suspected deepfake attacks on organizations or individuals, digital forensics for legal cases requiring technical analysis of video authenticity, and media verification by technical journalists with expertise to interpret detailed results.
Check the official site for the current access model, which may include free tiers for research, specific licenses for academic use, or commercial options. Verify terms regarding commercial use and legal admissibility of detection results if deploying for formal proceedings.
Get started with Deepware
Winston AI
Winston AI targets content authenticity verification for writers, bloggers, publishers, and marketing teams, focusing on publishing and digital marketing contexts rather than academic integrity enforcement.
AI detection covers both text and images, with support for multiple languages expanding usefulness beyond English content markets. A Chrome extension enables easy document scanning during editorial workflows. API access supports workflow integration for larger publishing operations. Readability scores complement AI detection, providing holistic content quality assessment. The tool is designed specifically for content authenticity verification rather than misconduct enforcement, reflecting different ethical considerations than educational tools.
Trade-offs include a focus on text and image content without audio or video deepfake detection capabilities, so organizations needing comprehensive multi-modal coverage must combine it with other tools. Accuracy concerns persist, with false positives possible on human-written content exhibiting technical or formulaic characteristics. Detection effectiveness varies by AI model and writing style as generation technology advances. The tool should not serve as the sole verification method for high-stakes publishing decisions where reputational or legal consequences are significant.
Appropriate use cases include publisher verification of freelance writer submissions ensuring contracted work meets originality standards, content marketing team quality control maintaining brand voice authenticity, SEO content authenticity checks verifying content meets search engine guidelines, and blog editorial workflows where editors review submissions before publication.
Pricing offers subscription plans for individuals and teams with various usage tiers. Verify commercial licensing terms and API access details on the official site, as features and pricing evolve with the platform.
Get started with Winston AI
Originality.AI
Originality.AI positions itself as a comprehensive content authenticity platform for publishers, content agencies, and SEO professionals, combining AI detection with plagiarism checking and readability analysis in a unified workflow.
Comprehensive text analysis includes AI detection, plagiarism checking, readability metrics, and fact-checking features providing multiple content quality dimensions. Team collaboration and workflow management features support agencies and publishing teams with multiple contributors. Bulk content scanning handles large volumes efficiently. A Chrome extension integrates into browser-based workflows. API access enables integration into custom content management systems and editorial tools.
Limitations focus on text exclusively, without image or multimedia detection. AI detection accuracy carries inherent uncertainty and may flag legitimate content, requiring editorial judgment. Pricing based on content scans can accumulate quickly for high-volume users processing hundreds of articles monthly. Detection effectiveness naturally decreases as AI writing tools improve, requiring ongoing platform updates to maintain reliability.
Best-fit scenarios include content agency quality assurance ensuring client deliverables meet standards, publisher editorial workflows reviewing submissions before publication, SEO content audits verifying site content authenticity for search engine compliance, freelancer hiring due diligence evaluating candidate portfolios, and brand content authenticity verification protecting reputation.
Pricing follows a credit-based model with subscription options—users can purchase credits for individual scans or subscribe for monthly credit allocations. Team plans distribute credits across multiple users. Verify current pricing and commercial terms on the official site as the platform evolves.
Get started with Originality.AI
Illuminarty
Illuminarty specializes in AI-generated content detection for creators, platforms, and moderators, with particular strength in visual media verification through an accessible web interface.
Detection algorithms cover both AI-generated images and text content. Image analysis includes deepfake detection across various generation methods, with visual heatmaps showing which regions appear manipulated. Text detection helps identify AI-written content. A browser-based tool requires no installation, lowering technical barriers. Batch processing supports reviewing multiple items efficiently. Detection confidence scores indicate result reliability, providing useful context for human review.
Trade-offs include specialization in images and text without comprehensive audio or full video stream analysis, so platforms needing complete multi-modal coverage still require additional tools. Detection accuracy varies significantly by generation method and quality—some techniques are detected reliably while others evade detection. False positives may occur on heavily edited but authentic photos, especially those using filters or compositing. Less suitable for enterprise-scale deployment compared to platforms like Hive or Sensity.
Ideal uses include content creator verification of image authenticity when sourcing references or investigating potential copying, social media moderator spot checks on reported images, digital artist protection against AI copying of their style, and journalism fact-checking of viral images circulating online.
Check the official site for current pricing models, which may include free tiers for limited use and paid plans for higher volume. Verify commercial use terms before business deployment, as licensing may restrict certain applications.
Get started with Illuminarty
Other Notable AI Detectors
The AI detection landscape includes additional emerging tools and frameworks beyond our primary 13. Hugging Face hosts various AI detection models as open-source research tools for developers comfortable with technical implementation. University research labs at MIT, Stanford, Berkeley, and elsewhere often publish public detection tool demos showcasing cutting-edge research, though these may lack production reliability.
OpenAI's own AI classifier was discontinued but indicates ongoing research interest from model creators themselves in detection capabilities. Spectrum Labs offers platform moderation tools including some AI detection features. Numerous browser extensions and open-source projects on GitHub target specific detection tasks, though quality and maintenance vary widely.
The landscape evolves rapidly with new tools launching, improved models releasing, and some tools being discontinued or acquired. Readers should verify current availability and capabilities rather than relying solely on historical information. Specialized tools exist for niche use cases—academic paper mill detection, AI-generated code detection, deepfake detection for specific languages or regional contexts—but these fall beyond the scope of this general guide focused on mainstream tools serving broad user bases.
Best AI Detectors by Use Case
Selecting the right AI detector depends critically on your specific use case, risk level, and workflow requirements. The following scenario-based recommendations connect tool capabilities to user needs.
Best AI Detector for Newsrooms and Fact-Checkers
Newsrooms face intense pressure to verify authenticity of user-submitted content, investigate viral media during breaking news, maintain editorial credibility, and avoid spreading misinformation. They require fast turnaround times, explainable results suitable for editorial decisions, and tools aligning with journalistic ethics standards around transparency and fact-checking rigor.
For professional newsroom workflows, TrueMedia.org is a strong choice given its explicit fact-checking focus, transparency about methodology and limitations, and alignment with journalistic standards. The non-profit model ensures mission alignment with public interest rather than profit maximization. For newsrooms requiring more comprehensive multi-modal detection at scale with enterprise support, Reality Defender or Hive are well-suited options providing robust capabilities with API access, faster processing, and commercial support structures.
These tools offer a practical balance of multi-modal support across images, video, and audio with processing speed suitable for breaking news. Explainability features help editors make defensible editorial decisions about content publication. Integration possibilities with newsroom CMS and existing fact-checking workflows reduce friction. Licensing terms explicitly permit editorial use without restrictive limitations.
Key features from detailed reviews supporting newsroom use include API access for automated screening of high-volume user submissions, confidence scoring helping editors prioritize review of most suspicious content, audit trails documenting verification steps for editorial standards, and clear licensing terms for publication contexts.
Critical limitations remain: no tool provides 100% accuracy, so editorial judgment and multi-source verification must complement detection. Detection should inform but not replace traditional fact-checking rigor including source verification, expert consultation, and corroborating evidence. Newsrooms should establish clear policies about how detection results factor into publication decisions.
Best AI Detector for Universities and Educators
Educational institutions need tools balancing academic integrity enforcement with student privacy and procedural fairness. Minimizing false accusations that damage student trust while deterring AI misuse requires careful tool selection. LMS integration enables seamless workflows fitting existing course management. Compliance with FERPA and student data protection laws is non-negotiable. Transparency about detection methods and limitations helps students and faculty understand appropriate use.
For educational contexts, GPTZero offers education-first design with an accessible free tier for individual educators plus institutional subscriptions for broader deployment. The focus on student privacy and appropriate educational use distinguishes it from general-purpose tools. Turnitin provides institutional-scale deployment with mature privacy protections, extensive LMS integrations, and established policies meeting educational compliance requirements. Copyleaks serves as a strong alternative combining AI detection with plagiarism checking and now image detection, offering robust LMS integrations and educational pricing.
These tools are among the most widely adopted and practically useful options in education, thanks to their seamless LMS integrations with Canvas, Moodle, Blackboard, and other platforms educators already use. Educational pricing models and institutional licenses fit school budgets and procurement processes. Student privacy compliance is built into platform design rather than retrofitted. Reporting formats suit academic misconduct procedures with explainability helping educators make fair decisions. Support resources specifically address educational use cases rather than generic implementation.
From our comparison table, key factors include ease of use for educators without technical expertise, pricing accessibility for education budgets, and integrations fitting existing workflows. Detailed review sections highlight privacy policies addressing FERPA compliance and licensing terms permitting educational use without commercial restrictions.
Emphasizing critical limitations is essential: AI detection must be one data point among many in academic integrity investigations, never the sole determining factor. False positives are mathematically inevitable and require instructor review with student conversation. Tools should complement rather than replace educational conversations about responsible AI use, academic integrity values, and learning objectives. Institutions should establish clear policies about detection tool use, student notification, and appeal processes.
Best AI Detector for Enterprises and Compliance Teams
Enterprise requirements differ substantially from education or personal use. Verifiable audit trails enable compliance documentation for regulatory reviews. Integration with existing security and compliance workflows reduces implementation friction. Support for regulated industries—finance, healthcare, legal—requires specific privacy and data handling capabilities. Scalable deployment across departments and geographies needs centralized management. Clear commercial licensing avoids legal complications. Vendor support and SLAs provide accountability and issue resolution.
For enterprise contexts, Reality Defender provides comprehensive multi-modal detection with enterprise features including detailed audit logging, team management, and commercial support. Copyleaks serves document and communications review needs covering text and images, with strong privacy controls suitable for regulated industries. Hive excels at platform and user-generated content moderation for enterprises operating communities or marketplaces.
Enterprise advantages of these tools include robust API and SDK options enabling custom integration into existing security stacks, audit logging documenting every detection action for compliance reviews, team management features supporting departmental deployment with appropriate permissions, clear commercial licensing removing uncertainty about permitted uses, vendor support and professional services helping with implementation and troubleshooting, and compliance with SOC 2, GDPR, and industry-specific regulations like FINRA or HIPAA.
From our comparison criteria, key considerations include integration capabilities matching enterprise technology stacks, compliance features meeting regulatory requirements, licensing clarity for commercial contexts, and pricing models supporting enterprise scale. Detailed reviews provide information about API capabilities, privacy policies, data residency options, and vendor support structures.
Cost-benefit considerations matter significantly for enterprises: these tools carry substantial costs through licensing fees, implementation effort, and ongoing maintenance. However, they reduce liability risks from AI-generated content in contracts, communications, or public-facing materials. Reputational damage prevention alone can justify investment. We recommend pilot testing with specific use cases and conducting ROI analysis before full deployment, measuring costs against risk reduction and efficiency gains.
Best AI Detector for Content Creators and Influencers
Individual creators face distinct challenges: protection against deepfake impersonation and voice cloning damaging reputation, verification of content originality for brand partnerships requiring authentic work, accessible tools without enterprise pricing, simple interfaces for non-technical users, and fast results enabling timely responses to impersonation incidents.
For individual creators, AI or Not provides a free tier and simple interface covering images, text, audio, and some video formats suitable for quick verification. Resemble AI offers voice-specific protection for creators whose voice is their brand—podcasters, voice actors, audiobook narrators. Illuminarty serves content verification needs for visual creators and writers concerned about AI copying their style or work.
Creator-friendly features include no signup or low-cost access fitting individual budgets, intuitive web interfaces requiring no technical training, visual results easy to share with audiences or platforms when reporting abuse, and fast turnaround supporting rapid response to impersonation.
From our comparison table, ease-of-use ratings and pricing models highlight accessible options. Detailed reviews discuss specific content type support—whether tools cover images, audio, video, or combinations—and whether free tiers have sufficient limits for creator needs.
Important limitations: free and low-cost tools may have lower accuracy than enterprise options, accepting this trade-off for accessibility. Detection results may not be legally admissible for formal takedown demands or litigation without additional corroborating evidence. Creators should combine detection tools with platform reporting mechanisms using standard abuse report channels and legal counsel consultation for serious cases involving significant financial or reputational harm.
Best AI Detector for Everyday Users Checking Images and Videos
Casual users encountering suspicious content on social media face uncertainty about authenticity of viral content, concern about deepfake news or celebrity impersonations, lack of technical skills for complex tools, and no budget for paid subscriptions.
For everyday verification, we recommend AI or Not for its accessible interface and free tier covering images, text, audio, and some video formats, TrueMedia.org for comprehensive video and audio fact-checking without signup requirements, Illuminarty for images and text checking, and Deepware for video deepfake detection accessible through a browser.
These tools emphasize simplicity and speed through web-based interfaces requiring no installation, minimal learning curves with straightforward designs, and results suitable for personal decision-making about sharing or trusting content rather than formal proceedings.
Our comparison table's ease-of-use ratings identify most accessible options, while detailed reviews discuss free tier access, usage limits, and whether signup is required.
Setting realistic expectations is critical: free tools have inherent limitations in accuracy and features given resource constraints. Casual users should treat detection as one signal among many—complemented by reverse image search, consultation of fact-checking sites like Snopes, verification across multiple sources, and healthy skepticism—rather than definitive proof. Detection provides useful input for personal decisions but not courtroom-level certainty.
How to Choose the Right AI Detector for Your Workflow
Selecting an AI detector requires systematic evaluation of your specific needs, constraints, and risk tolerance. Follow these steps to identify the right tool.
Step 1: Clarify What You Need to Detect
Begin by specifying precisely which content types require detection in your workflow. Do you need to verify text including essays, articles, or communications? Images such as photos, graphics, or memes? Video including potential deepfakes or synthetic footage? Audio encompassing voice cloning or synthetic speech? Or combinations of multiple types?
Different tools specialize in different modalities. Multi-modal needs may require either a comprehensive platform or combining multiple specialized tools. Moving beyond "I need AI detection" to specific scenarios dramatically narrows appropriate options: "I need to verify student essays for AI writing" suggests text-focused educational tools; "I need to screen user-submitted videos for deepfakes" points to visual detection platforms; "I need to detect if my voice has been cloned" indicates audio-specific tools.
Understanding detection goals clarifies tool selection: are you preventing misuse in educational or platform contexts, verifying authenticity for journalism or legal proceedings, or protecting intellectual property as a creator or brand? Each goal has different accuracy requirements, privacy considerations, and workflow needs.
Document specific detection scenarios you face and estimate volume requirements—screening 30 student assignments weekly differs dramatically from processing 10,000 user uploads daily. These details directly inform whether you need free tools, individual subscriptions, or enterprise platforms.
Step 2: Assess Your Risk Level and Responsibilities
Risk assessment shapes tool requirements significantly. In educational evaluation contexts, false positives harm students through unfair accusations, requiring tools minimizing this risk even at cost of some false negatives. News reporting faces opposite pressures—false negatives spreading misinformation damage credibility, justifying more sensitive detection despite some false positives requiring editorial review.
Legal and compliance scenarios create liability when errors occur, necessitating enterprise-grade accuracy, audit trails, and vendor accountability. Personal use involves low-stakes verification where imperfect free tools suffice.
Consider legal and regulatory responsibilities: FERPA compliance is mandatory for educational institutions, GDPR and CCPA govern data handling in relevant jurisdictions, industry-specific regulations like FINRA or HIPAA apply in financial services and healthcare, and potential legal admissibility matters when detection results might be presented in proceedings.
Involve appropriate stakeholders in tool selection: legal counsel should review compliance implications, IT security must assess data privacy and security posture, HR needs input for employee monitoring policies to avoid labor law issues, and educational leadership should consider student impact and procedural fairness.
Remember that no AI detector is perfect. High-risk use cases require detection to be one input in human decision-making processes, never the sole determinant of consequential decisions about academic standing, employment, legal action, or content takedowns.
Step 3: Balance Accuracy, False Positives, and User Impact
Understanding the fundamental trade-off between false positives and false negatives is essential. More sensitive detection catches more AI content but produces more false positives, wrongly flagging human content as synthetic. Less sensitive detection reduces false positives but misses more AI content through false negatives.
Consider false positive impact in your specific context: falsely accusing a student of cheating damages trust and may violate due process; wrongly rejecting legitimate creator content harms livelihoods; unnecessarily flagging employee communications creates hostile work environments; blocking authentic user-submitted media frustrates community members.
Similarly assess false negative risks: missing deepfakes that damage reputation creates liability; failing to detect AI-written contracts or communications with legal implications exposes organizations to fraud; allowing academic misconduct to proliferate undermines educational integrity and devalues legitimate credentials.
The optimal balance varies by use case. Education may prefer lower sensitivity to avoid unfair student accusations, using detection for initial screening followed by conversation. High-security contexts may prefer higher sensitivity, accepting that human review must filter false positives to prevent genuine threats.
We strongly recommend pilot testing with known authentic and AI-generated samples from your actual use case to calibrate tool sensitivity for your specific needs and observe false positive/negative patterns in your real-world content.
Step 4: Check Privacy, Data Handling, and Legal Terms
Reading privacy policies and terms of service before uploading sensitive content to any AI detector is absolutely critical, yet frequently neglected. Never assume reasonable data practices—verify them explicitly.
Key questions to investigate: Does the tool store uploaded content? For how long—temporarily during processing or indefinitely? Is uploaded content used to train or improve detection models, potentially exposing your data? Can you opt out of training data use? Where is data stored geographically, since jurisdiction matters for compliance with data localization laws? Are there data breach notification policies if security incidents occur?
Specific privacy concerns vary by use case: student work is protected by FERPA with severe penalties for violations; patient information is subject to HIPAA with criminal liability potential; employee communications involve labor law protections and reasonable expectation of privacy; proprietary business documents require confidentiality to protect competitive advantages and client trust.
For highly sensitive scenarios, consider enterprise plans explicitly addressing data handling in contractual terms or on-premises deployment options keeping data within organizational control boundaries. Cloud SaaS tools, however convenient, introduce third-party data access that may be unacceptable for regulated content.
Check commercial use licensing explicitly: some free tools prohibit business use in terms of service or require attribution that may be impractical. Enterprise tools include explicit commercial licenses but often restrict certain use cases. Verify that your intended application is explicitly permitted.
Remember that terms can change. Periodic review of vendor policies is prudent for long-term tool deployments, especially when vendors are acquired or change business models.
Step 5: Evaluate Integrations, Reporting, and Workflow Fit
Assess how the detection tool fits into existing workflows rather than requiring new processes. LMS integration matters for educators using Canvas or Moodle. API access enables developers to build custom integrations. Browser extensions help writers using Google Docs or WordPress. CMS plugins support publishers using specific platforms. Security tool integration allows enterprises to incorporate detection into existing security stacks.
Seamless integration dramatically increases adoption. Tools requiring manual copy-paste between applications and separate interfaces create workflow interruptions that users resist or skip. Single sign-on, automated data flow, and unified reporting within existing tools users already use daily makes detection frictionless.
Evaluate reporting features carefully: Are results genuinely actionable with clear next steps, or just scores without context? Can reports be saved and shared with stakeholders for review? Are confidence scores and explanations provided to support human judgment? Can reporting be customized for different audiences—students versus administrators in education, employees versus legal counsel in enterprises?
Consider team collaboration needs if multiple people use the tool: Do multiple users need access with appropriate permission controls? Can detection workflows be standardized across the organization with templates or saved configurations? Are there administrative features for managing users, tracking usage, and generating organizational reports?
Document your current workflow steps in detail, identify precisely where detection should occur, then evaluate candidate tools based on integration capabilities at those specific workflow points. A tool with excellent detection but poor integration may perform worse than a less accurate tool that fits seamlessly.
Step 6: Pilot 2-3 Tools with Real-World Samples
Strongly avoid committing to tool purchase or full deployment without hands-on testing. Theory and marketing materials differ from practice—only real-world testing reveals whether a tool truly fits your needs.
Narrow to 2-3 candidate tools based on Steps 1-5, then run parallel pilot tests comparing them directly. Testing with actual content from your target use case, not generic examples, reveals real-world performance: real student assignments from your courses for education, actual published articles for journalism, typical user-generated content for platforms, representative documents for enterprise compliance.
Design pilots systematically: test with a mix of known authentic and known AI-generated samples to directly observe false positive and false negative rates; include edge cases like heavily edited content, non-native English writing, technical jargon, and content from your specific domain to identify limitations; process sufficient volume to observe patterns rather than judging from a handful of examples.
Involve end users who will use the tool daily: teachers testing educational tools provide insights administrators miss; moderators testing platform tools understand workflow friction; compliance teams testing enterprise tools identify reporting gaps. User feedback on usability and workflow fit often matters more than marginal accuracy differences.
Document pilot results systematically: record accuracy observations with specific examples of false positives and negatives; collect usability feedback from actual users; note integration challenges and workarounds required; project pricing based on actual volume to avoid budget surprises; assess vendor support responsiveness by asking questions during the pilot.
The best tool is the one that fits your specific workflow and risk tolerance, not necessarily the one with the highest general reputation or most features. A slightly less accurate tool that users actually adopt and use correctly outperforms a perfect tool that sits unused due to poor workflow fit.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can AI detectors reliably tell human and AI-written text apart?
A fundamental challenge persists: as AI models improve and users learn to paraphrase or edit AI outputs, detection becomes progressively harder. This creates an arms race dynamic where detectors continually adapt to new models, only for next-generation models to evade detection until detectors update again.
Detection is probabilistic rather than definitive. Tools provide confidence scores, not binary certainty. False positives flagging human writing as AI-generated and false negatives missing AI writing are mathematically inevitable given the statistical nature of detection. No commercial tool can guarantee perfect accuracy.
The implications are serious for high-stakes contexts. AI text detection should inform but never solely determine decisions about academic misconduct charges, employment termination, content rejection, or legal proceedings. Human review and multiple sources of evidence remain essential. Anyone accused based on detection deserves opportunity to present counter-evidence and have decisions made by humans considering all context. This aligns with independent analyses and academic commentary, which consistently emphasize that current AI content detectors are not fully reliable and should not be used as the sole basis for consequential decisions.
Research transparency varies widely across tools. Some vendors publish third-party testing results and invite academic scrutiny. Others provide only marketing claims without independent verification. The lack of standardized benchmarks makes comparing accuracy claims across tools extremely difficult, leaving users to rely on hands-on testing and user communities sharing experiences.
Are AI detection scores admissible as evidence in academic or legal disputes?
In academic contexts, detection scores alone are generally insufficient for academic misconduct findings under most institutional policies and principles of procedural fairness. Institutions typically require detection to be corroborated by other evidence including comparison with the student's previous writing style, interviews with the student demonstrating or failing to demonstrate subject matter knowledge, review of draft history or revision patterns, and consideration of alternative explanations. Well-designed academic integrity policies treat detection as screening tool rather than definitive proof.
In legal contexts, some courts may admit detection results as one piece of evidence but are unlikely to accept them as conclusive proof without corroboration. Expert witness testimony about detection methodology, error rates, and limitations may be required to establish foundation for admissibility. Opposing counsel will certainly challenge reliability and probe false positive rates. Standards like Daubert in U.S. federal courts require scientific evidence to be based on testable methodology with known error rates—criteria that commercial AI detectors may struggle to meet given proprietary methods and limited independent testing.
Procedural fairness principles apply whether in academic or legal settings. Anyone accused based on AI detection should have opportunity to review the evidence, present counter-evidence, cross-examine methodology, and have decisions made by human adjudicators considering all evidence rather than algorithmic outputs alone. Policies that treat detection scores as automatic findings violate basic due process principles.
The evolving nature of detection technology creates additional challenges. Tools that perform well today may fail tomorrow as AI generation advances. Results from tools no longer maintained or using outdated models may lack reliability. These factors complicate using detection evidence in proceedings that may occur months or years after initial detection.
How accurate are AI deepfake detectors in 2026?
Detection tool sophistication varies from research prototypes to commercial enterprise platforms, with corresponding differences in effectiveness. How recently the detector was updated to counter new generation methods critically impacts accuracy, as older detectors miss techniques that emerged after their training.
An arms race dynamic characterizes the field. As deepfake generation technology improves, detection must constantly adapt to remain effective. Accuracy against cutting-edge deepfakes is always lower than against older techniques because detectors lag behind the latest generation methods by months or years. By the time detection adapts to one technique, new methods emerge requiring further adaptation.
Realistic expectations acknowledge that the best commercial detectors claim high accuracy on controlled test datasets but real-world performance is inevitably lower. Test datasets rarely capture the full diversity of generation methods, quality levels, and content types encountered in practice. Detection succeeds more often than not against typical deepfakes but fails against sufficiently sophisticated examples.
Critically, absence of detection does not prove authenticity. Advanced deepfakes specifically engineered to evade detection may successfully do so, meaning negative detection results provide weak evidence. In high-stakes contexts like legal proceedings, political campaigns, or journalistic investigations, negative detection should not be treated as proof of legitimacy but rather as one data point requiring corroboration through other forensic methods.
We recommend using deepfake detection as a screening tool to flag suspicious content for deeper human investigation rather than as definitive authentication. Forensic analysis by human experts examining inconsistencies, consulting source verification, and considering context remains essential for high-confidence authenticity judgments.
Do AI detectors store or use my uploaded content for training?
Some tools, particularly enterprise and education-focused platforms, explicitly commit not to store content after processing or use uploads for model training. These tools often highlight data privacy as a competitive advantage and include specific contractual terms in enterprise agreements. Storage is limited to temporary processing, with deletion occurring within hours or days.
Other tools store uploads temporarily for processing and operational purposes, then delete them after a retention period. The specific timeframe matters—deletion after 24 hours differs substantially from 90-day retention. Review retention periods in privacy policies carefully.
Some platforms may use uploaded content to improve detection models, viewing this as necessary to keep pace with evolving AI generation. Better platforms offer opt-out capabilities allowing users to prevent training use. Free tools are more likely to use uploads for training as part of the value exchange for free access.
Privacy policies can and do change. A tool with strong privacy protections today may alter policies after acquisition by a different company or business model shifts. Users relying on specific privacy commitments should periodically review current terms, especially for ongoing use.
Particular concern is warranted for sensitive content including student educational records protected by FERPA, proprietary business documents that could benefit competitors if leaked, personal identifying information subject to GDPR or CCPA, confidential communications protected by attorney-client privilege or trade secret law, and intimate images that could be weaponized if breached. Never upload truly sensitive content to tools without verified enterprise-grade privacy protections and contractual commitments.
For critical privacy requirements, consider enterprise plans with explicit data protection agreements specifying handling practices, retention limits, and breach notification requirements. On-premises deployment keeps data within organizational control, eliminating third-party access entirely but requiring significant implementation effort.
Check data location and jurisdiction as well. Where is content processed and stored? Does it cross international borders, potentially triggering GDPR issues or data localization requirements in countries like China or Russia? Jurisdiction affects legal recourse if problems occur.
Can students or employees bypass AI detectors?
The implications for relying solely on detection are concerning. Detection should be one component of comprehensive approaches rather than the sole enforcement mechanism. For educational contexts, this includes designing assignments that are less amenable to AI shortcuts such as requiring personal reflection, specific local knowledge, or creative approaches difficult to specify in prompts. Emphasizing learning process over final products through milestones, drafts, and in-class work makes AI less useful. Teaching responsible AI use as a literacy skill rather than simply prohibiting it prepares students for real-world contexts.
An adversarial relationship focused solely on catching violators proves less effective than cultural and policy approaches creating intrinsic motivation for authentic work. Clear policies about acceptable AI use that distinguish between permitted assistance and prohibited replacement help students navigate gray areas. Education about academic integrity values and why they matter builds internal commitment. Formative assessments and draft review shift focus to development rather than only final products. Oral defenses or exams verify that students understand submitted work.
Interestingly, some evasion methods require sophistication that itself demonstrates learning. Using advanced prompting techniques, iterative editing, and integration of multiple sources to create detection-resistant content involves critical thinking and synthesis skills that represent genuine learning outcomes, complicating judgments about academic integrity violations.
The reality is that over-reliance on detection creates an endless cat-and-mouse dynamic consuming time and resources. Better approaches design systems where AI misuse is harder, less beneficial, or less tempting than authentic work. Combining detection with positive incentives for original work, educational conversations about AI ethics and professional integrity, and assignment design valuing process and critical thinking creates multiple overlapping protections rather than single points of failure.
Are there privacy risks when uploading sensitive content to AI detectors?
Terms of service may permit uses you find unacceptable, such as using uploaded content to train or improve models, potentially exposing your sensitive information. Subpoenas or legal demands could compel vendors to produce stored data in litigation or investigations, even if you consider it confidential. Cross-border data transfers may occur when vendors use international cloud infrastructure, triggering complex compliance obligations under GDPR, data localization laws, or industry regulations.
Certain content categories demand extreme caution. Student educational records are protected by FERPA in the United States, with severe penalties for violations and potential loss of federal funding for institutions. Personal health information is subject to HIPAA with criminal liability possible for violations. Financial records trigger requirements under regulations like GLBA. Proprietary business documents could benefit competitors if leaked. Personal identifying information creates identity theft risks. Intimate images could be weaponized for harassment or extortion if breached.
We recommend never uploading truly sensitive content to free or public AI detection tools without verified enterprise-grade privacy protections including contractual commitments about data handling, specified retention limits and deletion procedures, audit rights allowing you to verify compliance, breach notification requirements providing timely warning if incidents occur, and data processing agreements meeting GDPR or similar regulatory standards.
Review vendor privacy policies thoroughly for specific commitments. Look for security certifications like SOC 2 Type II or ISO 27001 indicating professional security practices. Investigate breach notification history—has the vendor experienced publicized incidents? Check where data is stored and processed, ensuring compliance with applicable data localization laws.
For highly sensitive scenarios, consider alternatives to cloud-based detection. On-premises detection tools keep data within organizational control but require infrastructure and expertise. Enterprise contracts with stringent data protection agreements and possibly dedicated infrastructure provide stronger protections than multi-tenant SaaS. In some cases, avoiding AI detection entirely in favor of other verification methods may be most prudent when privacy risks exceed benefits.
Organizations subject to GDPR, CCPA, FERPA, HIPAA, or industry-specific regulations must ensure AI detector use complies comprehensively with data protection requirements. This typically requires involving legal and privacy officers in tool selection and deployment, completing vendor risk assessments, negotiating appropriate contractual protections, and documenting compliance measures for regulatory audits.
What should I do if an AI detector flags my legitimate work as AI-generated?
Immediate response steps include documenting your writing or creation process as thoroughly as possible. Collect drafts showing progression, research notes and outlines used in development, edit history from document platforms, time-stamped versions, and any other artifacts demonstrating authentic creation. Prepare to discuss your work in detail to demonstrate subject matter knowledge and explain creative choices that only the actual creator could articulate.
Request human review by an actual decision-maker rather than accepting an automated result as final. In educational contexts, request a meeting with your instructor or academic integrity officer. In employment contexts, escalate to human resources or appropriate management. For freelance situations, invoke dispute resolution procedures in your contract. Explain that detection tools have known false positive rates and that your case warrants individual review.
Ask what evidence beyond the detection score supports the allegation. Detection alone should never suffice for negative consequences. If no corroborating evidence exists—your work aligns with your previous style, you demonstrate clear understanding in discussion, drafts show authentic development—the detection result should be questioned rather than blindly trusted.
Understand your rights in different contexts. Students typically have academic due process rights including presumption of innocence until proven otherwise, right to review evidence and present counter-evidence, appeals procedures, and representation during proceedings. Employees may have employment contract protections, labor law rights, or union representation. Freelancers may have contract terms specifying dispute resolution procedures and evidentiary standards.
Certain writing styles are more prone to false positives, creating systemic fairness concerns. Non-native English speakers whose vocabulary and sentence structures differ from native speakers often trigger false positives. Formulaic or technical writing in fields like engineering, science, or law may appear AI-generated due to specialized terminology and conventional structures. Specific academic or professional conventions can resemble AI patterns. These factors should be considered in human review processes, not dismissed.
Being proactive helps if you know your writing style may trigger false positives. Document your process from the start rather than trying to reconstruct it after accusation. Maintain drafts and version history showing iterative development. Consider discussing your writing approach with evaluators before submission, establishing baseline expectations about your style. In educational settings, visit writing centers or meet with instructors during drafting to establish your authentic voice.
Emphasize that detection alone should never be the sole basis for negative consequences. Research and best practices uniformly recommend human judgment considering all evidence rather than algorithmic outputs. Push back firmly but professionally against policies treating detection as automatic proof.
If false positives affect many people systematically—multiple students in a class falsely flagged, numerous employees wrongly accused—escalate the systemic issue. The tool or its sensitivity settings may need adjustment, or the tool may be fundamentally inappropriate for your context. Institutions should pilot tools carefully before full deployment to identify such problems before harming people.
Can I rely on a single AI detector for critical decisions?
All detectors have imperfect accuracy with inevitable false positives and false negatives resulting from the probabilistic nature of detection. Different detectors frequently produce conflicting results on identical content because methodologies vary. Detection methodology is typically proprietary rather than peer-reviewed, limiting independent verification of accuracy claims. New AI models may evade detection entirely until detectors update, creating windows of complete ineffectiveness.
A multi-layered verification approach is essential for high-stakes decisions. Use AI detection as a screening tool identifying content warranting closer review rather than as definitive judgment. Combine detection with other evidence including writing style analysis comparing to known authentic samples, interviews or oral examinations probing understanding, subject matter testing requiring demonstration of knowledge underlying the work, draft history revealing development process, plagiarism checking detecting copied content, and reverse image search for visual content. Involve human expert judgment in final decisions rather than delegating to algorithms. Consider consequences and ensure procedural fairness for those accused, including opportunity to respond and present counter-evidence.
Some scenarios permit more reliance on single detectors when stakes are lower. Low-stakes personal verification deciding whether to trust social media content carries minimal consequences if wrong. Preliminary screening before deeper investigation uses detection efficiently to prioritize review efforts. Content moderation where human review follows positive detection creates a two-stage process preventing automated errors from causing final harm.
For high-stakes cases, consider using multiple detectors to triangulate. If two or three different tools with independent methodologies agree, confidence increases, though certainty still remains elusive. If tools disagree significantly, that uncertainty should inform decision-making by prompting additional investigation or declining to take action without better evidence.
The technology evolves rapidly. What works today may become less effective within months as AI generation improves and new models emerge. Ongoing monitoring and tool updates are necessary for sustained effectiveness. Establish review schedules to reassess tool performance and consider whether accuracy remains adequate for your use case.
Build policies treating detection as one input in human decision-making processes rather than determinative evidence. Train decision-makers to interpret detection results appropriately, understand limitations, seek corroborating evidence, and exercise judgment. Create accountability for decisions rather than hiding behind algorithmic outputs that provide convenient but false certainty.
Which AI detector should I start with if I'm new to this?
For text verification, GPTZero offers a generous free tier specifically designed for educators, making it ideal for teachers or professors exploring AI detection. It's suitable for both educators and students wanting to understand how detectors evaluate writing, allowing you to experiment without financial commitment.
For images and multi-modal content, AI or Not provides a simple interface with free tier covering images, text, audio, and some video formats. Illuminarty offers detection for both images and text accessible through a browser. Both help content creators or moderators understand detection capabilities and limitations across different content types.
For video deepfakes, TrueMedia.org operates as a free public tool designed for fact-checkers, making it accessible for anyone wanting to verify suspicious video content. Deepware offers browser-based deepfake video analysis with open-source components.
For audio and voice, Resemble AI may offer trials or demos allowing experimentation with voice detection, though free options are more limited in this category given the specialized nature of audio analysis.
Experiment with known examples to build understanding. Test tools with content you know is AI-generated versus authentic to observe performance and become familiar with report formats. Try edge cases like heavily edited AI content, formulaic human writing, non-native English text, and technical documents to understand false positive and false negative patterns specific to your content domain.
Read tool documentation and educational resources about AI detection to build conceptual understanding of how detection works and why limitations exist. Many tools provide explainer articles or videos helping users interpret results appropriately.
Join communities where others share experiences. Educator forums discuss academic integrity tools with practical tips. Content creator groups share experiences with deepfake protection. Industry-specific communities in journalism, compliance, or specific technical fields exchange best practices and tool recommendations.
Keep experimentation low-stakes. Avoid making important decisions based on detection until you understand tool behavior through hands-on testing. Use the learning phase to clarify your specific needs, volume requirements, accuracy expectations, and workflow integration needs.
After understanding detection capabilities and limitations through free experimentation, assess whether free tools suffice for your needs or whether your use case justifies investment in paid tools offering better accuracy, support, compliance features, and integration capabilities. Many users find free tools adequate for occasional personal verification while professional and institutional uses require paid solutions.
How much do AI detectors typically cost?
Free tiers exist for many tools suitable for occasional individual use. GPTZero, AI or Not, and TrueMedia.org all offer free access with usage limits appropriate for individual teachers, students, content creators, or casual verification. These enable experimentation and low-volume use without budget requirements.
Consumer and individual subscriptions targeting educators, writers, bloggers, and small teams typically range from very affordable monthly costs comparable to basic software subscriptions up to moderate monthly fees for more comprehensive features or higher usage limits. Tools like GPTZero paid tiers, Copyleaks individual plans, Winston AI, and Originality.AI fall into this category.
Professional and institutional subscriptions serving schools, universities, publishers, and mid-size businesses scale to moderate or significant annual costs based on user seats, student enrollment, or usage volume. Institutional Turnitin licenses, enterprise Copyleaks, and organizational GPTZero plans require budget planning and often procurement processes.
Enterprise platforms including Reality Defender, Hive, and Sensity use custom pricing at significant annual commitment levels, typically including professional services, implementation support, and ongoing vendor management. These require formal procurement with contract negotiation and budget approval at senior levels.
Pricing model variations include monthly or annual subscriptions with unlimited or tiered usage limits, credit-based or pay-per-scan models charging per document or upload, API usage-based pricing charging per request or tiered by volume, and institutional site licenses for universities based on student FTE or organizational size.
Educational discounts are common and sometimes substantial, recognizing budget constraints in education. Many tools offer 50% or greater discounts for educational institutions or teachers. Universities may already subscribe to tools like Turnitin through institutional licenses negotiated centrally, making them free at point of use for individual faculty.
Pricing changes frequently as markets evolve and tools adjust positioning. Always verify current pricing on official sites rather than relying on outdated information. Free trials or pilot programs are often available for evaluation before purchase commitments, and should be requested for any significant investment.
Calculate total cost of ownership beyond just subscription fees. Include staff time for training and workflow integration, which can exceed tool costs for complex deployments. Consider potential costs of false positives through appeals processes, re-grading, or damage to relationships. Account for opportunity costs if the tool doesn't fit workflows and ends up unused despite budget spent.
Free tools may suffice for low-stakes personal use where imperfect accuracy is acceptable. Critical applications including academic integrity systems, regulatory compliance, brand protection, and journalistic verification often justify investment in more accurate and supported paid tools. The decision should balance costs against risks and consequences of detection failures in your specific context.
What is the future of AI detection technology?
The arms race between AI generation and detection will certainly continue, possibly indefinitely. Periodic detection improvements will be followed by generation advances that evade detection, requiring further detector updates in endless cycles. Some experts question whether reliable detection is even possible long-term as AI generation approaches human-level quality across dimensions that matter for detection.
Increasing sophistication on both sides appears certain. Generation models will incorporate techniques specifically designed to evade detection. Detection methods will become more sophisticated, potentially using multi-modal analysis examining content holistically rather than in isolation, looking for subtle patterns across text, images, audio, and video together.
Digital watermarking and authentication standards may emerge as alternative approaches. AI generation platforms could embed cryptographic watermarks or authentication metadata proving content origin and modification history. Standards like C2PA (Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity) aim to create technical infrastructure for content authenticity without requiring detection of synthesis. This shifts from adversarial detection toward cooperative transparency.
Regulatory and legal developments will shape the landscape. Governments may mandate detection capabilities for certain platforms, require disclosure of AI involvement in content, or establish liability frameworks for undisclosed AI content in specific contexts. The EU AI Act and similar regulations emerging globally will influence detection technology development and deployment.
Novel detection approaches under research include identifying AI "fingerprints" inherent to specific models or generation methods that persist even through editing, blockchain or cryptographic proof of authenticity systems, and biometric-style analysis of creative patterns unique to individual humans.
Significant challenges loom. Completely reliable detection may prove impossible as AI generation quality approaches or exceeds human capabilities in increasingly many domains. The false positive problem may worsen as human creative expression becomes more diverse while AI-generated content becomes more sophisticated, narrowing the distinguishing characteristics. Privacy and surveillance concerns arise if detection becomes pervasive, with chilling effects on legitimate AI-assisted creativity.
Society will likely need to adapt beyond purely technical detection. Policy frameworks clarifying acceptable AI use in different contexts may prove more important than trying to detect and punish all use. Education teaching responsible AI use, proper attribution, and critical evaluation prepares people for AI-augmented futures. Cultural norms around transparency about AI involvement may evolve, with disclosure becoming standard practice rather than something to hide or detect. Media literacy and critical evaluation skills become essential life skills as detection reliability remains imperfect.
For readers navigating this landscape, staying informed is crucial. Follow vendor updates and product releases, read research publications from academic labs studying detection, and monitor industry news covering emerging tools and techniques. Participate in professional communities sharing experiences and best practices. Periodically reassess tools to ensure they remain effective for your needs as technology evolves.
The fundamental tension between the value of AI assistance and the need for authenticity verification will persist. Tools will improve, but perfect solutions remain elusive. Human judgment, ethical frameworks, and adaptive policies will remain essential alongside whatever technical detection capabilities emerge.
Discover More AI Tools
Explore our comprehensive directory of AI tools, carefully curated and reviewed by experts to help you find the perfect solution for your needs.